Efficient wastewater treatment is a cornerstone of sustainable development, addressing the crucial need for ecological preservation and public health enhancement. According to a report by the United Nations, approximately 80% of the world's wastewater is discharged into the environment without adequate treatment, leading to severe environmental degradation and health risks. The Wastewater Treatment Industry plays a pivotal role in mitigating these impacts by employing advanced technologies and practices designed to reclaim and recycle water resources effectively.
Dr. Emily Warner, a leading expert in the Wastewater Treatment Industry, emphasizes the urgency of the situation: "Investing in efficient wastewater treatment systems is not just an environmental imperative; it is a pathway to a sustainable future that fosters resilience against climate change and supports healthy communities." As populations grow and urbanization intensifies, the demand for innovative wastewater management solutions becomes increasingly critical. By enhancing our wastewater treatment capabilities, we can safeguard ecosystems, replenish freshwater sources, and ensure that future generations inherit a healthy planet.

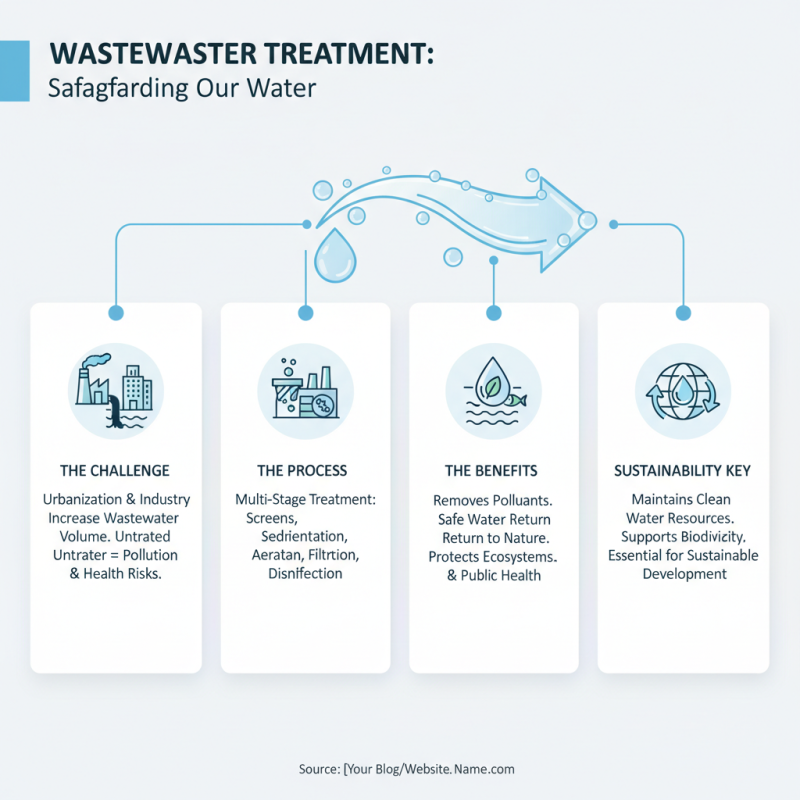
Wastewater treatment plays a vital role in safeguarding our water resources, an essential aspect of sustainable development. As urbanization and industrial activities continue to rise, the volume of wastewater generated has increased significantly. Untreated wastewater poses severe risks to both human health and the environment, contaminating rivers, lakes, and aquifers. Effective wastewater treatment methodologies remove harmful pollutants, enabling the safe return of water to the natural cycle and helping to maintain clean water sources for ecosystems and communities alike.
Moreover, treated wastewater can serve as a valuable resource, particularly in water-scarce regions. By reusing and recycling treated water for agricultural, industrial, or recreational purposes, we can reduce the overall demand for fresh water sources. This not only conserves vital water resources but also minimizes the environmental impact associated with extracting and transporting fresh water. The integrated approach of wastewater treatment thus aligns with the principles of sustainable development, ensuring that future generations have access to the clean water necessary for life and economic prosperity.
Water scarcity is a pressing global issue that affects billions of people and hampers sustainable development efforts. According to the United Nations, by 2025, an estimated 1.8 billion people will live in regions with absolute water scarcity, while two-thirds of the world’s population could be under water-stressed conditions. These statistics underscore the urgent need for effective wastewater treatment solutions to address this critical challenge. Efficient treatment of wastewater can significantly alleviate the pressure on freshwater resources by recycling and reusing water, thereby ensuring a sustainable supply for both communities and ecosystems.
Moreover, the importance of wastewater treatment extends beyond merely addressing scarcity; it plays a vital role in protecting public health and the environment. Untreated wastewater contaminates waterways, posing threats to aquatic life and human health. By investing in advanced treatment technologies, communities can transform wastewater into a valuable resource, reducing pollution and restoring natural ecosystems. This not only benefits local biodiversity but also enhances resilience against climate change impacts. As the global population continues to grow, prioritizing wastewater treatment becomes essential for fostering a sustainable and equitable future.
Untreated wastewater poses significant dangers to public health and ecosystems. When wastewater is discharged into water bodies without adequate treatment, it introduces a variety of harmful substances, including pathogens, nutrients, and toxic chemicals. This contamination can lead to the spread of waterborne diseases such as cholera and hepatitis A, which can disproportionately affect vulnerable populations, particularly in developing regions. The burden of these diseases strains healthcare systems and exacerbates poverty, highlighting the urgent need for effective wastewater management.
Moreover, the ecological impacts of untreated wastewater are profound. Nutrient overload from phosphates and nitrates can result in eutrophication, leading to harmful algal blooms that deplete oxygen in water bodies, causing dead zones that threaten aquatic life. Additionally, toxic substances can disrupt aquatic ecosystems, affecting biodiversity and the overall health of marine environments. The loss of biodiversity not only diminishes the resilience of ecosystems but also impacts the livelihoods of communities that depend on these resources for food and economic activities. Therefore, efficient wastewater treatment is essential not only for safeguarding public health but also for preserving the vital ecosystems that support life on Earth.
Efficient wastewater treatment plays a pivotal role in promoting sustainable development, especially when considering its economic benefits. According to the United Nations, approximately 80% of all wastewater generated globally is discharged into the environment without adequate treatment, leading to significant economic and environmental consequences. By investing in modern wastewater treatment technologies, municipalities can save up to 50% in operational costs compared to traditional methods. This cost-efficiency is not only beneficial for local economies but also helps prevent costly environmental remediation efforts in the future.
Resource recovery from wastewater presents further economic advantages. The World Bank estimates that the market for biogas generated from wastewater treatment can reach $90 billion by 2025. This resource can be harnessed to produce energy and potentially meet local energy demands, significantly reducing the reliance on fossil fuels. Additionally, recovering nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus can facilitate sustainable agriculture practices, reducing the need for synthetic fertilizers and thus lowering agricultural costs.
Embracing efficient wastewater treatment methods ultimately yields a dual benefit: it cuts costs while promoting a circular economy that conserves precious resources.
The regulatory frameworks governing wastewater management are crucial in ensuring that treatment processes are effective and sustainable. Governments around the world have established various laws and regulations that mandate specific standards for wastewater treatment. These frameworks often emphasize the importance of protecting water bodies from pollution, thus ensuring the health of ecosystems and communities. By setting strict discharge limits and promoting comprehensive monitoring systems, regulatory bodies encourage facilities to adopt advanced treatment technologies and practices, reducing the negative impacts of wastewater on the environment.
In addition to regulatory measures, innovations in sustainable wastewater management are reshaping the field. These advancements include the development of new treatment processes that utilize natural processes, such as constructed wetlands and bioreactors, which are both cost-effective and environmentally friendly. Moreover, emerging technologies like membrane filtration and nutrient recovery systems contribute to a circular economy by reclaiming valuable resources from wastewater. These innovations not only enhance the efficiency of wastewater treatment but also align with sustainable development goals, facilitating a more resilient and eco-conscious approach to managing water resources in the face of growing global challenges.
| Dimension | Importance | Innovations | Regulatory Framework |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water Quality Improvement | Prevents waterborne diseases | Bioremediation techniques | Clean Water Act compliance |
| Resource Recovery | Promotes circular economy | Nutrient recovery systems | EU Waste Framework Directive |
| Energy Efficiency | Reduces operational costs | Anaerobic digestion | Renewable Energy Standard |
| Public Health | Ensures community safety | Smart monitoring systems | Safe Drinking Water Act |
| Sustainable Practices | Protects ecosystems | Constructed wetlands | Global Water Partnership guidelines |






